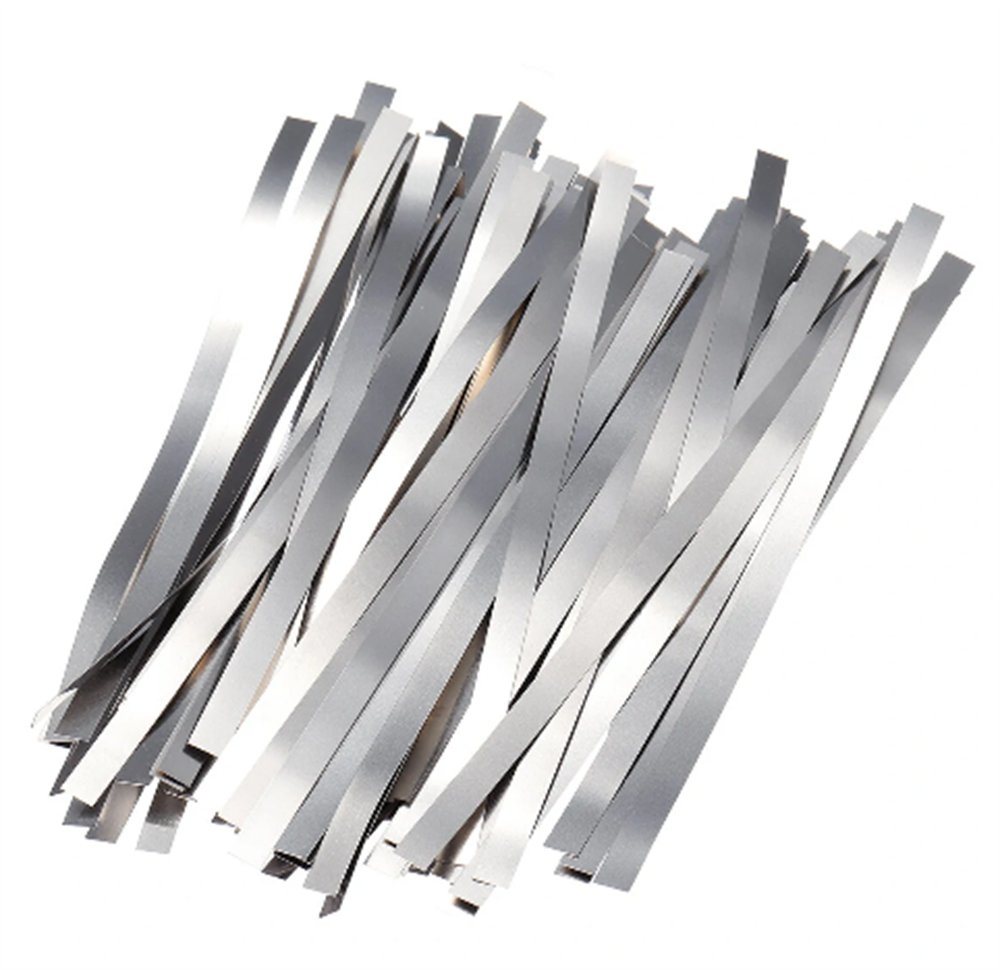


 Our company Principle is " Quality first, Customer first". CHANGZHOU DLX ALLOY CO, LTD was established in 2002 and has got Iso9001 International Quality Management System Certificate and SGS Certificate. Our factory is professional in researching and producing special alloy material. From melting, drawing, heat treatment, finishing and testing .We offer nickel-based, copper-based, and iron-based alloys, including super alloy, welding materials, anti-corrosion alloy, precision alloy, FeCrAl alloy, NiCr alloy, CuNi alloy, thermocouple and Foam Metal etc, in the form of wire, strip, ribbon, bar, tube, plate
Our company Principle is " Quality first, Customer first". CHANGZHOU DLX ALLOY CO, LTD was established in 2002 and has got Iso9001 International Quality Management System Certificate and SGS Certificate. Our factory is professional in researching and producing special alloy material. From melting, drawing, heat treatment, finishing and testing .We offer nickel-based, copper-based, and iron-based alloys, including super alloy, welding materials, anti-corrosion alloy, precision alloy, FeCrAl alloy, NiCr alloy, CuNi alloy, thermocouple and Foam Metal etc, in the form of wire, strip, ribbon, bar, tube, plate 1, We're able to design and develop the product what our customers require and meet their requirements through providing the appropriate engineering drawings or samples. 2, We can provide the products within a week after payment. 3, Wecan provide sample of the products customer need. 4, We always insist on "Quality first, Customer first" as our business philosophy.
1, We're able to design and develop the product what our customers require and meet their requirements through providing the appropriate engineering drawings or samples. 2, We can provide the products within a week after payment. 3, Wecan provide sample of the products customer need. 4, We always insist on "Quality first, Customer first" as our business philosophy.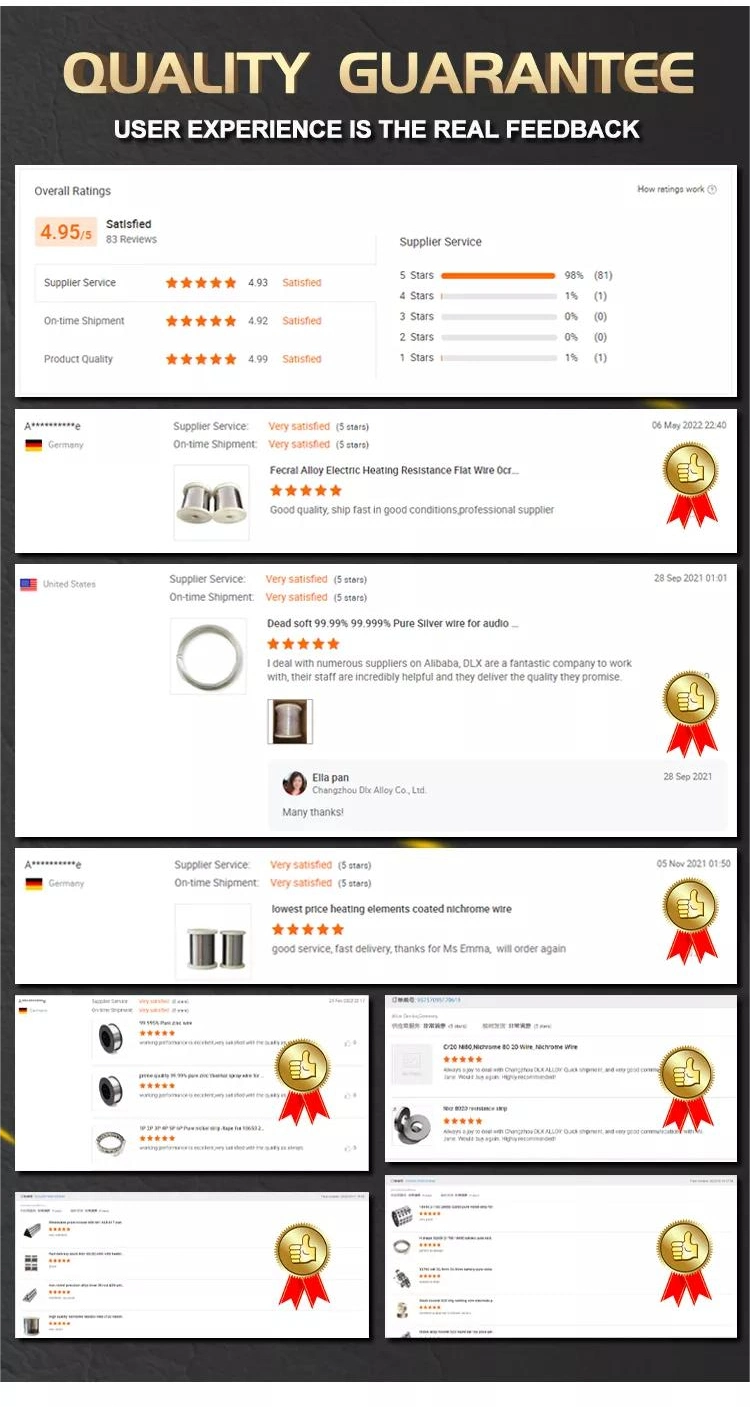 Question1: Are you a trading company or manufacturer? Answer: We're manufacturer. Question2: Could you help to design the product? Answer: Yes, we have excellent R&D team, OEM/ODM orders are all welcome. Question3: Could you supply samples? Answer: Yes, wecould supply samples according to your requirement. Question4: could we visit your factory? Answer: Sure, factory visit is warmly welcome.
Question1: Are you a trading company or manufacturer? Answer: We're manufacturer. Question2: Could you help to design the product? Answer: Yes, we have excellent R&D team, OEM/ODM orders are all welcome. Question3: Could you supply samples? Answer: Yes, wecould supply samples according to your requirement. Question4: could we visit your factory? Answer: Sure, factory visit is warmly welcome.| Molecular Weight | 107.87 |
| Appearance | Silver |
| Melting Point | 961.78 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2162 °C |
| Density | 10490 kg/m3 |
| Solubility in H2O | N/A |
| Electrical Resistivity | 1.586 microhm-cm @ 20 °C |
| Electronegativity | 1.9 Paulings |
| Heat of Fusion | 2.70 Cal/gm mole |
| Heat of Vaporization | 60.7 K-Cal/gm atom at 2212 °C |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.37 |
| Specific Heat | 0.0566 Cal/g/K @ 25 °C |
| Tensile Strength | N/A |
| Thermal Conductivity | 4.29 W/cm/K @ 298.2 K |
| Thermal Expansion | (25 °C) 18.9 µm·m-1·K-1 |
| Vickers Hardness | 251 MPa |
| Young's Modulus | 83 GPa |




